Join our webinar, Protecting Your Information with Microsoft Information Protection, Thursday, February 4, 1 p.m. eastern
Why does Information Protection matter?
Information Protection is the process of securing digital information without restricting the organization’s capability to use their data for business purposes or compromising consumer and end-user privacy. The significance of data protection rises as the amount of data created or stored continues to grow at astonishing levels. Data breaches cost companies on average more than $3.8 million and more than one quarter of companies over the next two years will experience a recurring breach (Auth0.com, 2020). Equifax, one of the largest credit bureaus in the US, experienced a data breach that exposed about 147.9 million consumers data. LinkedIn, one of the major social networks for business professionals, suffered from a data breach of 6.5 million passwords that were resold on a Russian hacker forum (CSO Online, 2020). Marriott, a hospitality company, endured a security breach that exposed 5.2 million guests’ data. Marriott could have avoided this breach by protecting their data at the file level and by implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) for employees attempting to access sensitive data (Auth0.com, 2020).
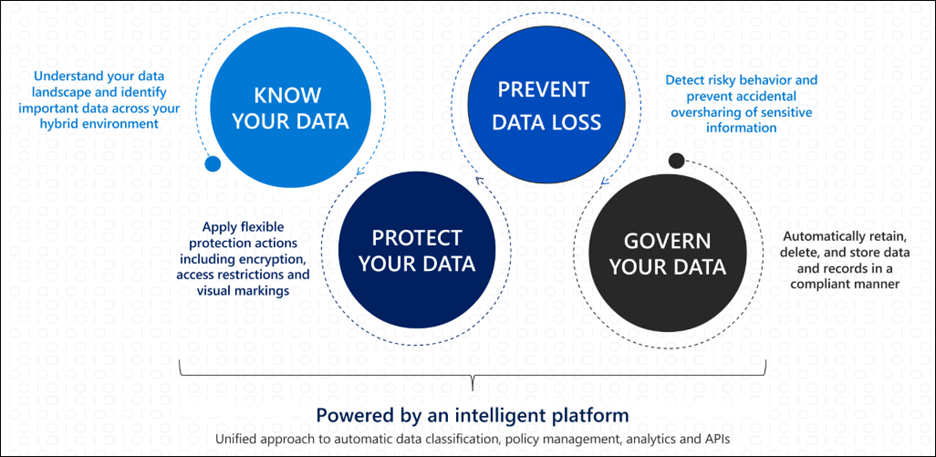
Most organizations experience issues with identifying, classifying, and protecting their data. It’s these businesses that will also have challenges protecting the data, especially organizations that do not want their data leaving their environment by email or a third-party file transfer site. Thus, the question arises; How can data safely leave an organization’s environment?
What is Microsoft Information Protection (MIP)?
Microsoft Information Protection (MIP) helps a business keep their data secure. Let’s start with some key definitions:
- Microsoft Information Protection (MIP) – A framework for products and integrated capabilities that use the same labeling store (“unified labels”) and help protect the organization’s sensitive information
- Data classification – Identifies items that have a sensitivity label, a retention label or have been classified as a sensitive information type and the actions that users are taking on them
- Sensitivity labels – A single solution across apps, services, and devices to label and protect data as it travels inside and outside the organization
- Encryption – The process of converting information or data into a code, especially to prevent unauthorized access
- Auto-labeling – The ability to save a document or send an email and have it automatically labeled based on the content within the document or email
- Sensitive information types – Identifies sensitive data by using built-in or custom regular expressions or a function, together with corroborative evidence that includes keywords, confidence levels and proximity
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) – Multi-factor authentication is a process where a user is prompted during the sign-in process for an additional form of identification, such as to enter a code on their cellphone or to provide a fingerprint scan.
MIP addresses business concerns regarding data protection by creating safeguarding controls and measures for the document at the file level. It also protects the data by classifying a document or email with a sensitivity label, which can be configured to encrypt the document or email and mark the document/email with a header, footer or watermark. When a file becomes encrypted and leaves the organization’s environment, the individual attempting to open the file outside of the organization will not be able to view the content without the appropriate credentials and permissions.
MIP can auto-label a document/email based on the content within the file once that document is saved. There are currently two different methods for automatically applying a sensitivity label:
- Client-side labeling is when users edit a document or create an email (also reply and forward) and use a label that is configured for auto-labeling office applications.
- Service-side labeling, also known as auto-labeling for data at rest, is when content is already saved in SharePoint Online, OneDrive or email. This is when an auto-labeling policy is used, and because this labeling is applied by services rather than application, there is no need to worry about what application users have.
There are over 100 pre-defined sensitive information types and users can create customized sensitive information types. Microsoft 365 applications that support sensitivity labels can perform actions when Microsoft detects a sensitive information type. For instance, personnel can create a Word document and insert a credit card number in the content of the file. MIP will detect this match when the document is saved, and an auto-label action can be initiated by the MIP policy. Sensitivity labels can encrypt a document so only individuals within a certain group can view that document. A user who is outside of that group, but still part of the company, will not be able to view the contents of that document.
Meeting today’s compliance standards and regulations
Compliance is critical in today’s world for a number of reasons, including:
- Avoid fines and penalties
- Protects a company’s business reputation
- Enhances a company’s data management capabilities
- Yields insights that promote operational benefits
- Enhances company culture
- Supports access controls and accountability
Regulations are rules that are enforced by governmental agencies that set the standard for what a company can and cannot do in business. The degree of compliance is up to every business based on their risk management. Not being compliant can result with a large fine, which s must be considered when assessing their risk management. Additionally, there is always the potential loss of reputation for failing to comply with applicable regulations.
As our society depends more and more on data and information systems, many regulations have a requirement for information security. Losing credit card or health information can be serious for both the company and consumers involved. When most of a company’s assets are information, it is vital to protect it accordingly.
Other key benefits of Microsoft Information Protection
MIP helps a company understand and control where the data goes and how it is being used. It can also help a company:
- Prevent data being copied, modified, or stored without a user knowing
- Prevent unauthorized users from viewing data
- Provide more control over data by understanding who is using the data and how they are using it
- Meet compliance requirements i.e., retaining files for a certain amount of time
A key benefit of MIP is its’ granular level of detail, which assists a company with GDPR compliance and encryption. GDPR states that a data breach does not need to be reported to the affected people if the data controller implemented appropriate protective measures such as encryption. This is because encrypted information is unreadable without the encryption key, so no key information would be exposed.
Microsoft Information Protection (MIP) helps organizations with classifying and protecting their data. Since MIP protects the data at the file level, the risk of an external user trying to exfiltrate data is significantly reduced.
To learn more about our Microsoft consulting solutions, contact us.